EDDI 19 Technical Training Day – Learning Objective 1: Task 2 – Running automated tests on Jenkins
Overview
Teaching: 5 min
Exercises: 10 minQuestionsObjectives
- How do I ensure my code is tested before it is deployed?
- Running automated tests within Jenkins
- Displaying the results of the tests in Jenkins
Task 2 – Running automated tests on Jenkins
Requirements
To complete this task, your coffee machine should have at least one unit test.
Running the tests
Jenkins has a selection of tools that can process test results in a variety of different formats and display them in the interface. The main format we are interested in are Junit test results. These are exported from many frameworks.
Jenkins also integrates with SonarQube, a static analysis framework that analyses code for common issues such as security and maintainability issues. When integrated into the Jenkins pipeline SonarQube can be configured to only let builds continue when quality gates are passed.
If testing is integrated with the standard lifecycle of your frameworks build tools, collect the results using a post stage after the build has completed. If your language tooling runs a test as a separate command from the build add a new stage with a post block collecting the test results. The post block will look like this:
post {
always {
junit 'junit.xml'
}
}
On success the Jenkins page for your component should look like this:
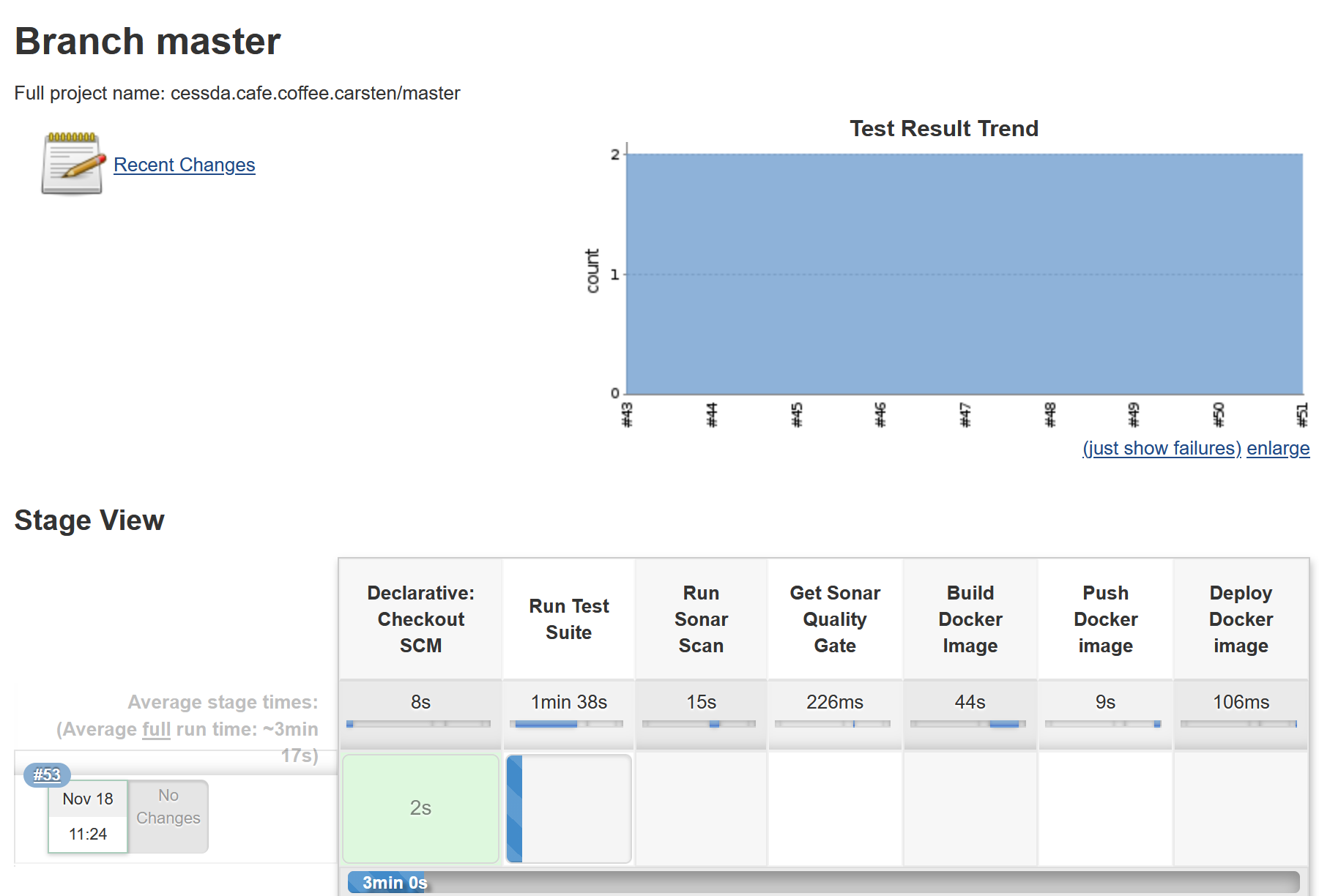
A panel has been added to the Jenkins view showing the test results for current and previous builds. If tests fail, selecting the section of the graph that has the failed tests will open a view that will show what tests failed, the reason and a stack trace.
Notes for Maven
Because of Maven’s integration with Jenkins when using a withMaven step, post stages don’t need to be declared. Test results will be automatically gathered by Jenkins and displayed in the view for each branch.